Organic Protein
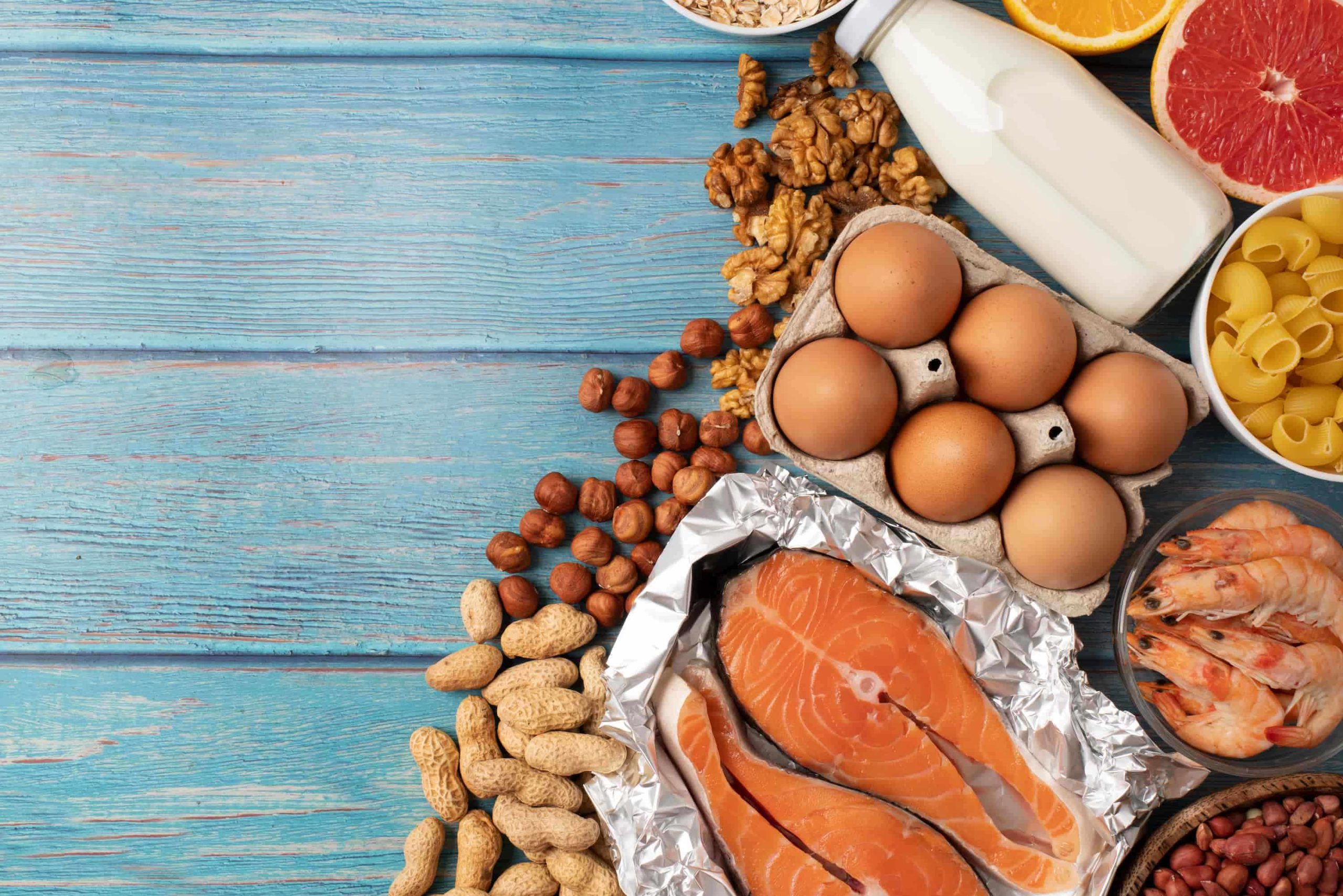

As an athlete, it’s important to understand the importance of organic protein in your diet. Protein is a crucial nutrient that plays a vital role in building and repairing muscle tissues.But with so many protein options out there, it can be overwhelming to figure out which ones are the best for your individual needs. That’s why we’re here to help.
In this post, we’ll explore the top organic sources of protein for athletes and provide guidance on how much protein you should be consuming and when. So, whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting out on your fitness journey, read on to learn how protein can take your performance to the next level. Don’t forget to read to the end of the blog for more tips and information!
| Fact Table | |
|---|---|
| Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth | When you engage in physical activity, your muscles undergo stress and need time to repair and rebuild. Protein provides the necessary building blocks (amino acids) for this process. |
| Athletes require more protein than sedentary individuals | Depending on the type of activity and intensity level, athletes may need anywhere from 1.2-2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. This is higher than the recommended daily intake for sedentary individuals. |
| Timing of protein intake is important | Consuming protein after a workout can help to maximize muscle protein synthesis and aid in recovery. Additionally, spreading protein intake throughout the day can help to maintain a positive nitrogen balance (a measure of protein status in the body). |
| High-quality protein sources are recommended | Animal-based sources of protein (meat, dairy, eggs) are considered “complete” proteins, meaning they contain all essential amino acids. Plant-based sources of protein may be incomplete and require combining different sources to ensure adequate intake of all essential amino acids. |
| Overconsumption of protein may have negative effects | Consuming too much protein can lead to dehydration, kidney damage, and increased risk of certain chronic diseases. It is important to balance protein intake with other macronutrients and overall caloric intake. |

What is protein and why is it essential for athletes?
Protein is a crucial macronutrient for athletes, as it plays a fundamental role in muscle repair and growth. According to the Stanford Medicine Health Library, “Protein is one of the three macronutrients, along with carbohydrates and fats, that our body requires in large quantities for optimal health.” Proteins are made up of amino acids, and there are 20 different types of amino acids. Our body can produce some amino acids on its own, but there are others that we need to obtain from the food we eat. Therefore, consuming a diet rich in organic sources of protein is essential for athletes to meet their nutritional needs and support their athletic performance.
Why is Protein Essential for Athletes?
Protein is essential for athletes because it helps to repair and build muscle tissue, which is often damaged during exercise. When we exercise, we create small tears in our muscle fibers, and protein helps to repair and rebuild these fibers, making them stronger than they were before. Additionally, protein helps to support our immune system, regulate our hormones, and maintain healthy skin, hair, and nails.
How Much Protein Do Athletes Need?
The amount of protein that athletes need can vary depending on their individual needs, goals, and training regimen. In general, athletes need more protein than sedentary individuals to support muscle growth and repair. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends that athletes consume between 1.2 and 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. This means that a 150-pound athlete would need between 82 and 136 grams of protein per day.
Protein for Muscle Repair and Growth:
How does protein aid in muscle recovery and growth?
Protein aids in muscle recovery and growth through the process of muscle protein synthesis. During exercise, our muscles undergo stress and damage, which can lead to muscle soreness and fatigue. Protein helps to repair and rebuild damaged muscle tissue by providing the amino acids that are necessary for muscle protein synthesis. This process involves the body using the amino acids from protein to rebuild and create new muscle tissue. Additionally, protein intake can help to increase the production of anabolic hormones such as insulin and growth hormone, which also contribute to muscle growth and repair. By consuming adequate amounts of protein, athletes can support their muscle recovery and growth, ultimately leading to improved performance.
Protein for Energy
How does protein contribute to an athlete’s energy needs?
While carbohydrates are typically the main source of energy for athletes, protein also plays a role in meeting their energy needs. When the body runs low on carbohydrates, it can use protein as an alternative source of energy through a process called gluconeogenesis. During this process, the liver converts amino acids from protein into glucose, which can be used by the body as fuel. While protein is not as efficient at providing energy as carbohydrates, it can still be an important energy source during prolonged exercise or when carbohydrate stores are depleted. Additionally, consuming protein alongside carbohydrates can help to slow down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, providing a more sustained source of energy. However, it is important to note that consuming excessive amounts of protein for energy can lead to negative health consequences and should be avoided.

Protein Timing and Quantity
How much protein should athletes consume?
The amount of protein an athlete should consume depends on their individual needs, including their body weight, type of sport or activity, and training goals. However, as a general guideline, it is recommended that athletes consume between 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. It is also important to spread protein intake throughout the day, rather than consuming large amounts in a single meal.
when is the best time to consume it?
Timing of protein intake is also important for athletes. Consuming protein shortly before or after exercise can help to enhance muscle protein synthesis and improve recovery. Ideally, athletes should aim to consume a protein-rich meal or snack within 30 minutes to an hour after exercise. This can be in the form of whole food sources such as lean meats, fish, eggs, or dairy products, or protein supplements such as whey protein powder. Additionally, consuming protein before bed can also be beneficial for muscle repair and growth, as the body undergoes a period of repair and recovery during sleep.
It is important to note that while protein intake is important for athletes, consuming excessive amounts can have negative health consequences, such as kidney damage and increased risk of heart disease. Therefore, it is important to consume protein as part of a balanced diet and in moderation. Consulting with a registered dietitian or sports nutritionist can also be helpful in determining the appropriate amount and timing of protein intake for individual athletes.
Sources of Organic Protein
There are many sources of protein that athletes can incorporate into their diet, including:
- Lean meats such as chicken, turkey, and beef
- Fish and seafood
- Eggs
- Dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt
- Plant-based sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, and quinoa
What are the best food sources of protein for athletes?
There are many organic sources of protein that are beneficial for athletes, including:
- Lean Meats: Chicken, turkey, beef, and pork are all excellent sources of protein. Choosing lean cuts of meat can help to reduce the amount of saturated fat in the diet.
- Fish: Fish such as salmon, tuna, and sardines are high in protein as well as heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
- Eggs: Eggs are a versatile and affordable source of protein, with one large egg containing around 6 grams of protein.
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are all good sources of protein, with Greek yogurt being particularly high in protein.
- Plant-Based Protein Sources: Legumes such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of plant-based protein. Quinoa, tofu, and tempeh are also good options for vegetarians and vegans.
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds such as almonds, peanuts, and chia seeds are high in protein, as well as healthy fats and fiber.
It is important to note that not all organic sources of protein are created equal, as some sources may also be high in saturated fat or other harmful components. Therefore, it is important to choose a variety of protein sources and balance them with other healthy foods as part of a balanced diet.
Timing of Protein Intake
In addition to the amount of protein, the timing of protein intake is also important for athletes. Consuming protein shortly after exercise can help to maximize muscle repair and growth. This is because our muscles are most receptive to protein in the first 30 minutes to an hour after exercise. Athletes should aim to consume protein within this time frame to optimize their recovery and performance.
Supplements and Protein Powders
Protein supplements are a popular option for athletes looking to increase their protein intake, particularly for those who have difficulty meeting their protein needs through whole food sources alone. While protein supplements are not necessary for all athletes, they can be a convenient and effective way to ensure adequate protein intake, particularly in situations where whole food sources are not readily available or easily digestible.
When it comes to choosing a protein supplement, there are many options available on the market, including whey, casein, soy, and plant-based protein powders. Whey protein, derived from milk, is one of the most popular options and is considered a high-quality protein source due to its amino acid profile and fast absorption rate. Casein protein, also derived from milk, is a slower digesting protein that may be beneficial for promoting muscle protein synthesis over a longer period of time. Soy protein, derived from soybeans, is a plant-based option that is high in essential amino acids and may have additional health benefits, such as reducing cholesterol levels. Plant-based protein powders, made from sources such as pea, rice, and hemp, are also becoming increasingly popular due to their suitability for those following a vegan or vegetarian diet.
Ultimately, the best protein supplement for an athlete depends on individual needs and preferences. It is important to consider factors such as taste, cost, and potential allergens when choosing a protein supplement. Additionally, it is recommended to choose a supplement that has been third-party tested for quality and purity, as some products may contain harmful contaminants. As with any supplement, it is also important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating protein supplements into your diet, particularly if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Comparison between organic proteins and protein supplements

When it comes to meeting their protein needs, athletes have the option of consuming whole food sources of protein, such as meat, poultry, fish, and dairy, or using protein supplements. While both options can provide adequate protein intake, there are some differences to consider.
Organic proteins from whole food sources offer a range of nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and fiber, that protein supplements do not provide. Additionally, whole food sources of protein are typically more satiating than protein supplements, which may help athletes feel fuller for longer and reduce their overall calorie intake. Eating a variety of whole food protein sources can also provide a wider range of amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein that are needed for muscle repair and growth.
On the other hand, protein supplements can be a convenient and effective way to ensure adequate protein intake, particularly for athletes who have difficulty meeting their protein needs through whole food sources alone. Protein supplements are also more easily digestible and absorbed by the body compared to whole food sources of protein, which can be beneficial for post-workout recovery. Additionally, protein supplements can be a more cost-effective option compared to purchasing and preparing whole food sources of protein.
In summary, both organic proteins from whole food sources and protein supplements can provide adequate protein intake for athletes. The best option depends on individual needs and preferences, as well as factors such as cost and convenience. Incorporating a variety of protein sources, including both whole food sources and supplements, can help athletes meet their protein needs and support their performance goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, natural protein plays a crucial role in the performance of athletes. Protein is necessary for muscle repair and growth, and it also contributes to an athlete’s energy needs. Athletes should aim to consume a sufficient amount of protein through whole food sources, such as meat, poultry, fish, and dairy, as well as protein supplements if needed. The timing of protein consumption and the amount of protein needed varies depending on individual goals and activity levels. Incorporating a variety of protein sources can also provide a wider range of nutrients and amino acids. By prioritizing protein intake, athletes can optimize their performance and support their overall health and wellness.
FAQ
The recommended protein intake for athletes varies depending on their activity level and goals, but generally ranges from 1.2-2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight per day.
Yes, athletes can meet their protein needs through whole food sources such as meat, poultry, fish, dairy, legumes, nuts, and seeds. However, protein supplements may be a convenient and effective way to supplement the diet.
While immediate post-workout protein consumption may be beneficial for muscle recovery, the overall timing of protein consumption throughout the day is more important than the timing of a single meal.



